What is a Masters, How Long Do They Take and Why Do One?
A Master’s Degree is a popular academic qualification studied after completing an undergraduate degree. A Masters’s degree helps you explore a particular area or topic in greater detail to become a “Master” of the subject. In many cases, postgraduate study can also boost your chance of employment and earning potential by demonstrating that you possess advanced knowledge and critical thinking skills.
We have put together a comprehensive guide to help you understand what is involved in applying for, studying and your prospects and options once you have graduated with a master’s degree.
We focus on online postgraduate courses, but the information below also applies to on-campus Master’s degrees apart from fees and costs.
What Level is a Master’s Degree?
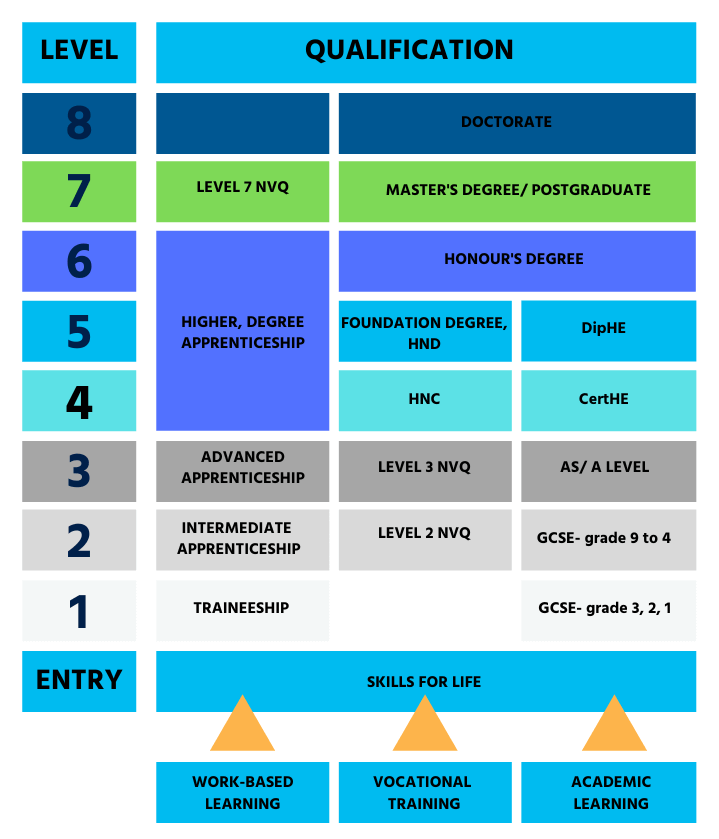
A master’s degree is level 7 in the UK qualifications framework. These courses are typically taken after completing a full undergraduate degree and before taking a PhD.
How Many Credits are in a Master’s Degree?
Under this system, a UK master’s degree comprises 180 CATS points (1,800 hours of study) at Level 7. In contrast, undergraduate degrees have 120 CATS points for each academic year of full-time study. CATS points are used alongside the level to qualify programmes and certificates.
UK University qualifications use a system of CATS points or credits to measure the number of learning hours on a course. This system makes it possible to compare courses. All credit-bearing courses in the UK quantify the number of hours of study required to gain the qualification. This process means that every 10 hours of study is equal to 1 CATS point or credit. This article has more information about CATS Points and Notional Learning.
What is a Postgraduate Qualification?
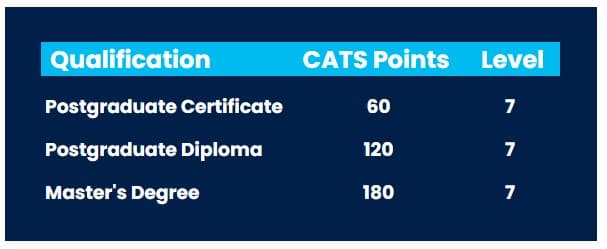
All education at level 7 or above can be called postgraduate study. There are three main certificate types in the UK at level 7- Postgraduate Certificates, Postgraduate Diplomas and full Master’s degrees.
It is common for master’s students to be able to exit a taught master’s degree at set points with either a Postgraduate Certificate or Postgraduate Diploma.
A Postgraduate Certificates are generally made up of 60 credits, whereas a Postgraduate Diplomas are made up of 120 credits.
For example, a Postgrad Diploma is a good option for students who want to gain a higher level qualification but do not want to complete a dissertation or research project.
What’s the Difference Between Taught and Research Master’s Degrees?
While Wikipedia lists over 100 certificate titles for Master’s degrees, all UK master’s can be broken down into two distinct groups- Taught Masters and Research Master’s degrees. Which type you take depends on your goals and reasons for postgraduate study.
Research-based Master’s degrees, as the name suggests, primarily focus on independent study and academic research. These courses are a stepping stone to a PhD and an academic career. The two main research masters titles are Master of research (MRes) and Master of Philosophy (MPhil)
Taught Master’s degrees still have a large amount of independent study, but the course is structured around modules and set pieces of work in the same way as undergraduate bachelor’s degrees. A tutor leads these taught courses, sets deadlines and instigates discussions. The final assessment is typically an independent research project. Taught Master’s degrees are mainly taken for professional and personal development, but graduates can go on to PhD programmes after completing this type of course.
What Do You Do on a Taught Online Master’s Degree?
The majority of online masters are taught as opposed to research masters. A taught online master’s is a similar learning experience to an undergraduate degree. The course is structured around modules and assignments that build on each other to become more involved and challenging as the course progresses. The final assessment is typically a major piece of independent research or a dissertation. This article has more details about what’s involved in online learning.
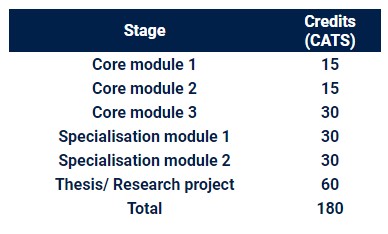
Taught masters are led by an academic, with set deadlines to submit assignments. Different courses and universities offer varying levels of flexibility and time to complete the course. The table below illustrates the module structure for a complete 180-credit master’s program.
How Long Does it Take to Get an Online Master’s Degree?
A master’s degree takes one academic year of full-time study. Some universities offer online Master’s that can be completed in one year, but this is not common. Instead, most online Master’s degrees are part-time, and either have a fixed two-year time frame or can be studied over two to five years.
Online courses are the most popular option for mature students looking to balance their careers while gaining a postgraduate qualification. You can use our part-time study calculator to see how you could fit a master’s degree into your schedule.
What Are The Entry Requirements To Study for a Masters In The UK?
Students usually take a master’s degree after completing an undergraduate degree. Typically, universities look for a 2:2 or above in a relevant subject as a minimum.
However, an undergraduate degree in a relevant subject is not required for conversion courses. So, for example, an applicant could have a 2:1 in English but still get accepted onto a Law or Psychology conversion course.
Entry requirements for postgraduate qualifications do not have the same level of government set regulation, meaning universities can be more flexible when assessing applications. Admissions teams may be able to give more weight to relevant career experience than previous academic qualifications taken many years ago.
When to Apply for a Master’s Degree?
Unlike undergraduate degrees, you can apply for a master’s at any time in the year. You apply directly to the university, and each university has its own deadlines and start dates. Generally, September is the most popular intake each year, but for online Master’s, there can be quarterly or even monthly starts dates.
It’s typically best to apply six months before any deadline, especially on competitive courses where there are usually more applications than places. Applying well in advance also means having enough time to arrange funding via student loans or other sources.
How to Apply to a Master’s Programme
You apply directly to the university for most Master’s courses. Each university has its own requirements and guidelines. Once you have narrowed down your choice of course, you should request the application pack or access it online. You need to make sure you read it carefully and understand exactly what is required.
The personal statement is an important part of the application, especially on competitive courses. We have a guide on how to write a strong personal statement that breaks the process down into 7 steps.
For some master’s programs, you may have an interview with one of the academics before a final decision to offer a place is made.
Depending on the university, you will generally need to submit a combination of the following.
- Completed application form
- Up-to-date CV highlighting professional skills
- Professional or academic references
- Personal statement
- Copies of previous qualifications and transcripts
- Proof of English language for non-native speakers
- Proof of identity
- Portfolio of work
It is common for people to apply before they have sat an IELTS test or requested work references. In this situation, a university will give a conditional offer of a place pending certain conditions being met, for example, upon receipt of suitable references or an IELTS score of 6.5 or above.
Getting a conditional offer can be a great way to confirm that you are suitable for the course and know that you will get a place before you book a test or ask your line manager for a reference.
What IELTS Score do You Need for a Master’s Degree?
Most universities look for an IELTS score of 6.5 for prospective Master’s degree applications. Some courses may accept an IELTS 6.0. However, this is less common. Postgraduate courses with demanding language components such as Law may require a 7.0 or 7.5. This guide on English language requirements for international students has more details about accepted tests and scores at UK universities.
How Much Does an Online Masters Degree Cost?
The costs of a master’s degree varies between universities and subjects. The maximum amount of student loan available for UK students is £11,836, with most online masters programmes priced around this amount. However, be aware that the tuition fees for specific business-related courses from prestigious universities can cost multiple times the loan amount available.
At most universities, tuition fees average around £8,000 to £12,000 for online programmes. You must have your Master’s degree funding in place before you start studying for your course, and it’s recommended to arrange funding during or before your application. Fees can generally be paid in instalments, but you need to check with the university you are applying to.
Check out our guide, funding options for higher education at UK universities, to understand what options are available for UK and International Students.
How Much is An Online Masters’s Degree UK for International Students?
The good news if you are an international student is that online Master’s degrees usually have a single fee for home and international students, unlike on-campus courses that cost thousands of pounds more.
What Is A Masters Degree FAQs – Common Questions About Postgraduate Study
Are UK Master’s Degrees Internationally Recognised?
Yes, UK Masters’s degrees are mapped to the Bologna Process. This means that they benchmarked against European equivalents on standards and quality. In addition, UK Master’s degrees are recognised in the United States as equivalent to US master’s degrees.
Can a Master’s Degree Help with a Career Change?
Yes, this is a popular reason people take Master’s degrees and postgraduate qualifications.
Specific careers and professions require an undergraduate degree in that area, for example, Law. However, if you have an undergraduate degree in English but want to practice law, you could take a conversion master’s in Law instead of a second three-year undergraduate degree.
These types of Masters’s courses are called conversion courses. These courses are taught masters and tend to give students a broad grounding in the subject area.
Our guide, different types of master’s programmes, has more information about conversion courses.
What are Graduate Prospects Like with a Master’s Degree?
A master’s degree can boost career prospects. It shows that you have achieved academic excellence and are willing to extend your knowledge and skills for personal and professional development. Employers value this investment that an employee has made in themselves.
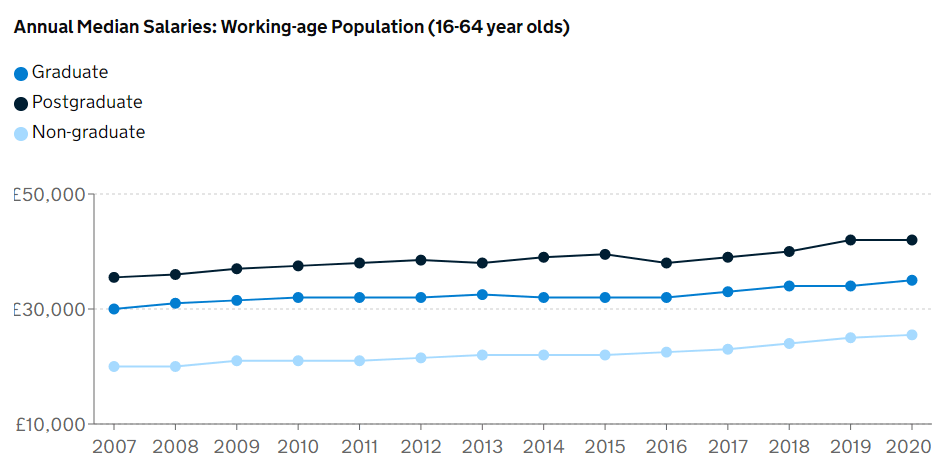
In addition to the personal development gained from the learning experience of a postgraduate degree, master’s level study positively impacts earning potential.
The UK Graduate labour market statistics 2020 clearly shows that postgraduates consistently earn more than undergraduates and non-degree holders.
What is the Difference Between an Undergraduate Bachelor’s Degree And a Masters’s Degree?
Bachelor’s degrees are level 6, while a master’s is level 7. This means that the work on a master’s is considered to be at a higher level. Whereas an undergraduate degree can be quite broad, a master’s qualification tends to be more focused on a specific topic within the subject area. In general the higher up in academia you progress the more specialised the area of study.
The structure of a taught master’s is similar to an undergraduate degree with set modules and assignments, whereas a research master’s is based on independent research and investigation. Another difference between graduate and postgraduate study is that Students in postgraduate courses are expected to be far more independent than undergraduate degree students.
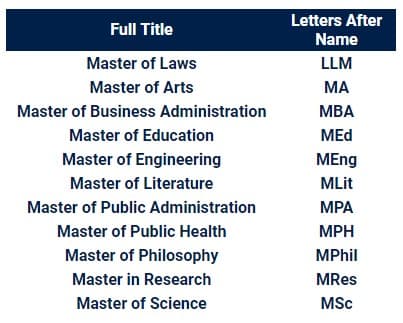
What Letters Can I Put After My Name with a Master’s Degree?
In the UK, the letters you can use after your name for positions, qualifications, memberships, or other status are called post-nominals. Once you have earned a master’s degree, you can use certain letters after your name. For example, if you hold a Master of Arts in English, using the letters MA after your name is acceptable.
UK universities award almost 50 certificate types for a complete Master’s course. These are some of the most common ones you will encounter in your search for a course.
What are the different names for a master’s degree?
A master’s degree is often just called a master’s. However, studies at this level get labelled in a number of different ways. Here are some of the most common terms you will come across when you are researching courses at this level
- Postgraduate study
- Postgrad degree
- Second cycle qualification
- Research programmes
- Advanced degrees
- Graduate degree
- Graduate programs
- Integrated masters
How Can I Fund a Master’s Degree?
If you are a UK resident, you may have access to government postgraduate loans, similar to the undergraduate student loan system. If postgraduate loans are not an option, funding choices for postgraduate study are,
- Commercial loans
- Company sponsorship
- Scholarships and grants
- Personal savings.
Do I Need A Master’s To Get A PhD?
Universities generally require PhD candidates to hold a master’s degree. It is standard practice for students to start a research master’s degree and, if their research meets set standards, progress their study to a full PhD. It is at this point that students can stop their research and graduate with a Master of Philosophy (MPhil) or Master of Research (MRes)
How Much Does A Masters’s Degree Increase Your Salary UK?
According to the 2019/20 UK government statistics, the median earning after five years of graduating with a taught master’s degree was £32,800.
This is a boost of £5,400 a year in additional salary compared to the average undergraduate salary of £27,400
Can You Do a Master with a 2:2
To be accepted on a competitive course at a top-ranking university, applicants typically require a 2:1 or above. However, some universities and courses will accept applications from holders of an undergraduate bachelor’s degree at 2:2.
Always check the admission requirements for each course you are interested in. If you have relevant work experience at the right level, it is worth speaking directly with the admissions team. They will be able to advise if they can take your work experience into account when assessing candidates.
Can You Do a Masters Without an Undergraduate Degree?
It is possible to be accepted to some master’s degrees without an undergraduate degree. However, this is only possible where the student demonstrates significant equivalent experience and certification.
For example, a business leader in a management position with professional certification, considered to be at the equivalent level to undergraduate study, gaining a place on a Leadership MA.
Gaining a place on a Masters without an undergraduate degree and relevant professional certification and experience is not possible.
What is a Master’s Degree Alternative?
Master’s degree programs are at Level 7. The main level 7 alternatives to a master’s degree in the UK are
- Level 7 award
- Level 7 certificate
- Level 7 diploma
- Level 7 NVQ
- Postgraduate certificate
- Postgraduate diploma
What is an Executive Master’s?
These are taught or research-based management courses designed for mid-career and senior professionals and are called executive master’s degrees. They are typically part-time and offer the flexibility to complete the course while working full-time. Online, part-time MBAs (Masters of Business Administration) are good examples of this type of course.
Executive Master’s degrees are usually the flagship courses offered by business schools, and places on these courses can be highly competitive.
Can You Do A Masters In Something Not Related To Your Undergraduate Bachelor’s Degree?
Yes, there are Masters’s degrees designed especially for this situation, Conversion Courses, and others that will accept relevant career experience.
Can You Do A Masters While Working Full Time?
Working full-time and studying for a Master’s degree is very common. Online, part-time masters are specially designed to meet this demand. Gaining a master’s degree while working part-time has become increasingly popular in recent years as the postgraduate student loan makes funding more accessible.
How Old Are Masters Students?
For part-time postgraduate study, 70% of students are over 30 and over.
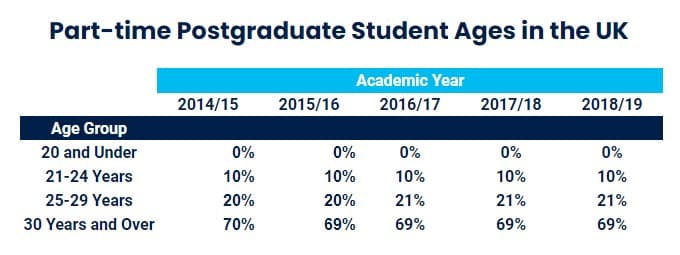
Source: HESA Higher Education Student Statistics
What Is The Age Limit For Doing Masters In the UK?
There is no upper age limit for a master’s degree in the UK. However, some master’s degree funding options do have upper age limits.
Postgraduate loans have an upper age limit of 60 years on the first day of the academic year that the course starts. Commercial loans available for higher education vary in their upper age limits. We have more information about funding options for international and UK-based postgraduate students.
What Is An Integrated Master’s Degree?
An integrated master’s is a four-year, full-time course that combines a bachelor’s degree with a master’s degree. Students can leave after year three with an undergraduate degree or continue to the Master’s degree program in year four.
How are Masters Graded?
Masters in the UK are graded as, Pass, Merit and Distinction. Students typically need to score 70% or higher to gain a distinction.
