Top-up Degrees Explained
A top-up degree is a way to gain a full undergraduate degree by combining previous certificates with a year of full-time study. As the name suggests, students who take these courses are topping up their qualifications with extra study.
Top-up degrees;
- recognise and build on previous studies.
- Award a full undergraduate certificate for one year of full-time study.
- Give access to postgraduate programmes and positively impact career progression.
Typically, students start a top-up course after completing a full level 5 qualification, such as a Higher National Diploma (HND) course or a Level 5 NVQ.
You can search for Online Top-up Degrees on this page by using the certificate options filter.

Qualification Levels- Where Does a Top-Up Degree Fit In?
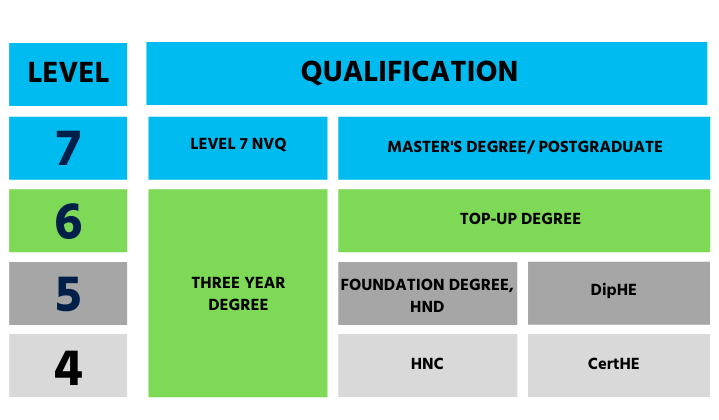
All credit-bearing certificates awarded in the UK fit into a scale of 0 to 9. For example, an undergraduate degree is level 6, and a master’s is level 7. A top-up degree is a level 6 qualification, the equivalent of the final year of a three-year bachelor’s degree.
The table below compares the levels of undergraduate study.
Top-Up Degree Structure
Most programmes have a starter module that acts as a refresher for academic skills. They cover essentials, such as academic writing and references. This first module benefits students returning to study or with limited essay writing experience.
The central units in the course will typically focus on the key topics and themes of the subject being studied. They also develop and practice the academic skills required for the final project.
The majority of these courses have honours in the title and have the designation BS (Hons) or BSc (Hons). The “Honours” part means that the course involves an independent piece of research and investigation submitted as a thesis or final project.
It is common for students to use the final project to focus on an area that will impact their career or help with a career change.
Below is an illustration of the module and credit breakdown of a Business Management BA (Hons) Top-up.
| Business Management BA (Hon) | Credits |
| Introduction to Academic Skills | 5 |
| Marketing Management | 10 |
| Accounting and Finance for Managers | 15 |
| Strategic Management | 30 |
| Final project | 60 |
| Total Credits at Level 6 | 120 |
Entry Requirements

To recap- A top-up degree is the last year of a standard three-year qualification. Therefore, to join these programmes, students must demonstrate that they have successfully completed the equivalent of the first two years of a degree. They can do this by submitting existing certification or, in some exceptional cases, demonstrating relevant career experience.
Standard certificates that are accepted are Higher National Diploma, NVQ or BTEC. So, for instance, if you hold an HND in engineering, you could join an engineering top-up degree.
Lists of Common Level 5 Certificates in the UK
- Diploma Of Higher Education (DipHE)
- Foundation Degree
- Higher National Diploma (HND)
- Level 5 Award
- Level 5 Certificate
- Level 5 Diploma
- Level 5 NVQ
If you are an international student or hold a qualification not listed above, you can still join a top-up degree if you can demonstrate that they are the equivalent of the first two years of a degree. In this situation, the admissions team will use a system of CATS points and the certificate level to assess the equivalency.
What Is the Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme (CATS)?
If you are investigating universities, you will likely come across CATS points. CATS stands for Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme. They were designed to enable students to transfer between different courses and institutions. The basic idea is that ten hours of study equals one credit or 1 CATS point.
In the UK, a full honours degree equals 360 CATS points, or 3,600 hours of study (360 CATS X 10 = 3,600 hours of study time). Each year of full-time study on a degree is worth 120 CATS points.
The admission teams will look at your existing transcripts and add up the CATS points at the appropriate levels when you apply. They are looking for 240 CATS points at levels 4 and 5.
In some cases, the admissions team may need to go through a formal mapping process with an applicant to accept them onto the programme.
Approved Prior Learning (APL)
If you are an international applicant or hold non-standard certificates such as professional exams, the admissions team will use a mapping process called APL to assess your application in this situation. APL stands for Approved Prior learning.
Admission teams will often work with guidelines created by Eccti (Formally NARIC) to address international certificates and map them into the RFQ framework. They use the tables created by ECCTI to understand the level and CATS points of international qualification.
The best advice for international students, or applicants with professional certification, is to speak directly with the admissions team to understand what options are available based on the certificates you hold.
Non-standard Applications
Because of the structure of these courses, they are an excellent way for mature students to gain a degree without studying for six or more years part-time.
If you are a working professional in a specialised or managerial role without a suitable level 5 qualification, it may be possible to base your application on your work experience.
To demonstrate work experience at a matching or higher level to an HND, applicants need to go through a process called APEL.
Accreditation Of Prior Experiential Learning (APEL)
APEL is a way the admissions teams can assess an applicant’s work or voluntary experience to ensure that they are at the right level to get the most out of a course.
The process can include, but is not limited to:
- A written proposal.
- Submitting a portfolio of evidence.
- Written statements.
- Work references.
- A viva and review by an independent panel of experts.
Each university in the UK sets its requirements and process around APEL. You may find that some do not offer this option at all. In contrast, others may have an established process for entry onto their top-up degrees.
However, be aware that there may be a cost incurred for an APEL. Due to the work and time involved in conducting an APEL, many universities charge a non-refundable upfront fee.
Benefits of Top-Up Courses
To recap, the benefits of a top-up degree are- They
- Can be completed in one year of full-time study;
- Build on previous study to award a full bachelor’s degree;
- Open up postgraduate study options;
- Help with career progression or career change.
In summary, they are great for mature students and working professionals looking to gain a BA or BSc degree and already have a related HND or foundation degree.
Top-ups are also an option for individuals who don’t hold a relevant two-year qualification but have appropriate knowledge and experience to achieve the award at universities that offer an APEL process for admission.
Most Common Questions- FAQ
Can You Use a Student Loan for a Top-Up Degree?
Student loans are available for top-up degree courses in the same way as complete degree programmes are for UK residents. The loan amounts can cover the tuition fees and are repayable only once you have graduated and are earning over a certain amount.
You can even get funding for a second degree in specific subject areas. You can find out more here.
Is a Top-Up Degree the Same as a Standard Degree?
While a top-up degree is shorter and has different entry criteria to a standard degree, the final certificate has the same recognition as a traditional three-year degree.
Specific subject areas do not offer top-up degrees- Medicine is an example. These specialist subjects require many years of in-depth learning that do not lend themselves to the format of a top-up degree.
Is a Top-up Degree Recognised?
In subjects where top-up degrees are available, employers and universities recognise and treat them in the same way as full undergraduate three-year degrees.
Top-up degrees from UK education providers are internationally recognised qualifications, the same as a full bachelor’s degree. Students often go on to take postgraduate courses after a top-up degree.
Can You Join a Master’s with a Top-Up Degree?
Yes, a top-up degree is a complete level 6 qualification. These certificates enable access to Level 7 courses, such as an MA, MSc and MBAs.
For example, you could join an MBA or MA in leadership upon completing a Business Management BA (Hons) top-up degree. You can Seach online Master’s courses here.
How Long Does a Top-Up Degree Take?
It will take a year of full-time study to complete and between 2 and 4 years of part-time study.
Each course will have its own guidelines on time frames and the required study hours. However, if you are studying full-time, you can build on your previous qualification to gain a complete degree in only 12 months.
Is a Top-Up Degree an Internationally Recognised Qualification?
Yes, they are fully recognised undergraduate qualifications and can be used to access Master’s level study. A top-up degree is a complete level 6 qualification that can be used for work permits and visas.
What Is the Difference Between a Foundation Degree and a Top-Up Degree?
Foundation degrees are level 5 qualifications, and top-up degrees are level 6. So you would generally take a foundation degree first, and after completing it, you would join the top-up degree.
What Does It Show on the Transcript of a Top-Up Degree?
The transcript will show all the units you have studied, the credit value, and the score when you graduate, totalling 120 credits. The other 240 credits of a UK degree will show as an APL or APEL credit.
How Are Top-up Degrees Graded?
All assessments are given a grade out of 100. At the end of the course, those scores show a final mark based on 100. Each university sets its cut-off points between classifications, but they are all broadly similar to the below.
- First Class Honours (1st, one or I) – 70% or higher
- Second Class Honours;
- Upper-division (2:1, 2i or II-1) – 60–69%
- Lower-division (2:2, 2ii or II-2) – 50–59%
- Third Class Honours (3rd, three or III) – 40–49%
